Residents of San Francisco and Phoenix have grown used to witnessing one thing that, a decade in the past, would have appeared magical. In some components of those cities, at sure instances, automobiles drive by with no person behind the wheel.
Driverless “robotaxi” companies choose up clients and ferry them to their locations with the assistance of cameras, sensors and software program that makes use of synthetic intelligence. Exams of absolutely driverless autos have been beneath approach in Phoenix since 2017 and in San Francisco since 2020.
Excitable movies posted on-line present clients embracing the novelty. However new potentialities deliver new questions. Whereas these real-world experiments are restricted in scope, they may assist resolve the way forward for highway transport all over the place. It is important that classes are realized and the outcomes opened to scrutiny.
A number of years in the past, when hype surrounding self-driving automobiles was enormous, some high-profile crashes introduced consideration to the ethics of experimenting with new applied sciences in public areas.
US states inspired experimentation by dropping regulatory boundaries, with cities, residents and transport policymakers having little say. After a interval of testing with security drivers, some automobiles at the moment are absolutely driverless.
Whereas the businesses study to drive safely in complicated environments, San Francisco and Phoenix are studying whether or not the expertise is creating extra issues than it guarantees to unravel.
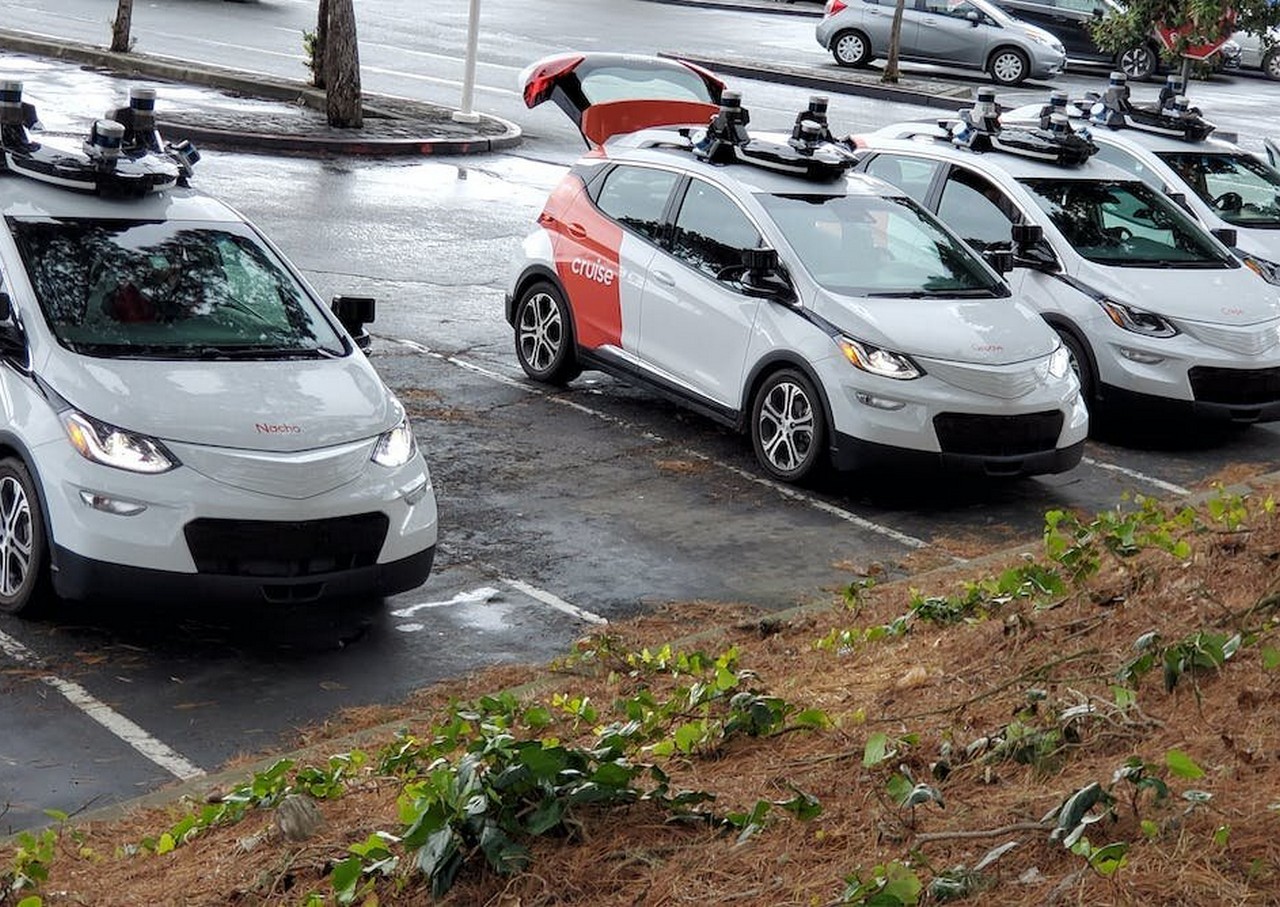
Cruise (owned by Normal Motors) is now working 30 driverless automobiles at evening in all however the busiest components of San Francisco. Simply earlier than Christmas, the corporate stated it wished so as to add extra automobiles, function through the day, and transfer into town’s busiest downtown space.
However San Francisco’s transportation authority raised objections. Within the final yr, Cruise automobiles have been concerned in numerous incidents that, whereas indirectly life-threatening, have been actually annoying for a metropolis making an attempt to go about its enterprise.
A Cruise automotive with no person inside was pulled over by law enforcement officials, who have been uncertain what to do. To the amusement of individuals filming, the automotive then pulled away from the confused cops.
Cruise automobiles have additionally annoyed town’s fireplace division by blocking fireplace vans and driving in the direction of hoses. In a single case, firefighters have been pressured to smash a automotive’s windscreen to get it to cease. The automobiles have impeded native buses, blocked junctions and stopped in the course of the highway, generally in teams.
Some incidents would have counted as on a regular basis snarl-ups if a human was behind the wheel, however the absence of anybody within the automotive to take duty has made it arduous for metropolis authorities to know what to do.
The streets of San Francisco
In nearly all circumstances, we solely learn about incidents due to on-line movies or experiences by native folks. There are few duties on the businesses to report efficiency or admit their foibles.
These incidents, and the absence of accountability, are clearly making an attempt the persistence of San Francisco’s transport planners. Fairly than a free-for-all, they wish to see what they name “restricted deployments with incremental expansions” in order that impacts could be assessed rigorously.
They might additionally wish to preserve driverless automobiles out of town’s busiest downtown core—and, crucially, wish to see extra data-sharing. This could make the self-driving experiment extra democratic, however cuts in opposition to the grain of the Silicon Valley strategy to “blitzscaling”—rising quickly to ascertain a monopoly.
Self-driving automotive firms would argue that the extra automobiles they’ve and the extra complicated their environments, the faster they’ll study to drive. This argument is premised on the concept that robotic drivers are similar to human drivers, however higher. In actuality, self-driving automobiles aren’t “autonomous autos,” as is usually claimed.
They depend on digital and bodily infrastructures that help their operation, in addition to groups of people behind the scenes doing the data-labeling, distant operation and buyer help that’s wanted to make them seem “driverless.” These automobiles work finest in car-friendly areas the place pedestrians and different highway customers behave predictably.
Altering the foundations
Even when driverless automobiles keep away from the errors that people make when drunk or distracted, they make differing types of errors. New modes of transport don’t simply add one other participant to the sport; they alter the foundations. When automobiles arrived in cities within the early twentieth century, pedestrians have been persuaded or bullied out of the best way and infrastructures have been remade to go well with the brand new expertise.
Within the twenty first century, many cities have been spooked by the speedy disruptions wrought by ride-hail firms resembling Uber and Lyft. We should keep away from sleepwalking into one thing comparable. For self-driving automobiles, we want a transparent sense of the trade-offs.
There might finally be security advantages. However in making life simpler for self-driving automobiles and the few folks prone to profit, we would make life tougher for everybody else.
Competitors for roadspace in dense cities is tight. As transport coverage skilled David Zipper has argued, most cities wish to see fewer automotive journeys general, and extra shared transit and bodily energetic journey resembling strolling and biking.
Self-driving automobiles could possibly be an issue for sustainability. The extra we study from real-world makes use of of the expertise, the better appears the mismatch between its purported options and the issues dealing with cities.
The UK is much less in thrall to tech firms, which supplies a chance for a extra measured dialogue. In 2022, I used to be a part of a staff led by the Middle for Knowledge Ethics and Innovation asking what a extra accountable strategy to self-driving car innovation could be. We suggested on security, data-sharing, transparency and making certain that the advantages are evenly unfold.
As self-driving automobiles broaden to extra locations, the social studying that occurs round them will probably be simply as essential because the machine studying that drives their computer systems. The experiment is going down in public, so we should be sure that its classes aren’t saved personal.
Supplied by
The Dialog